With the exponential growth of digital users, systems are designed to sustain the high load and be responsive under such load.
Earlier, systems were designed for the predictive load like 10k active users. With today’s demand, designing a system for predictive load is not a good approach, as it is hard to predict the load after some months or years. To meet these challenges, systems are designed to handle the elastic load, which could sustain under high load and still be responsive to requests.
Below are some points to consider for making the system highly scalable for the elastic load.
Adopting Microservice Architecture
The biggest problem with Monolith is scalability. Monolith Architecture allows vertical scaling of hardware like an increase in CPU, RAM, etc. But vertical scaling has some limitations. For example, we could have a maximum of 64 GB of RAM, 32-core CPU. Monolith architecture fails to serve unpredictable high load after some threshold.
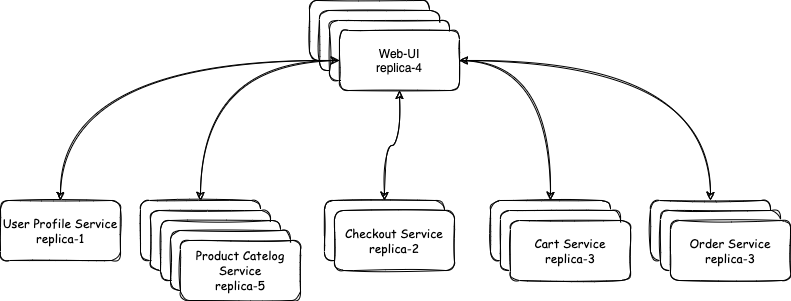
Microservice architecture is a style of designing architecture where a system is a collection of multiple small services based on its domain, characteristics, and team working on it. Each small service is a microservice that can be deployed independently and could have multiple replicas. The load gets distributed amongst these replicas. Major benefits of using microservice architecture are -
- Make the system highly scalable by scaling the number of replicas.
- Provide the ability for each microservice to scale differently. For example, On an e-commerce website, where product search service has more load than checkout service. In this case, the product catalog could have more replicas than checkout.
- In a monolith, the entire system is deployed on a single machine. In case of high load on a component affect other component’s performance, as resources are shared. Whereas each microservice has its dedicated resources.
Modern Cloud Deployment
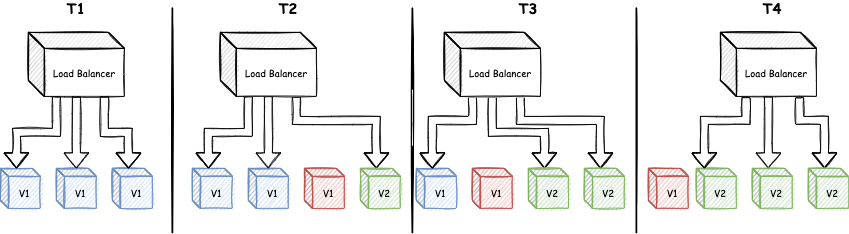
On-premise traditional deployment is not scalable under unpredicted high load, as limited resources are kept reserved for such incidents. It is recommended to use Modern Clouds like AWS, Azure, GCP, etc. These cloud providers offer high availability and provision to scale applications automatically under high load.
Auto-scaling is a popular feature, used for highly scalable systems. Where application replicas are scaled up or down automatically based on load
Polyglot Persistence
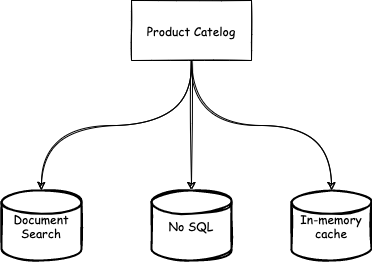
The microservice architecture enables building each microservice to have a different programming language and persistence. A microservice could use different persistence storage for data based on query or requirement. For example, A Product Catalog Service uses the following persistence -
- ElasticSearch for text-based search.
- Redis Cache for trending/featured products.
- NoSQL database for storing users/products/transactions.
- RDBMS for storing metadata for joins and reporting.
Asynchronous Messaging
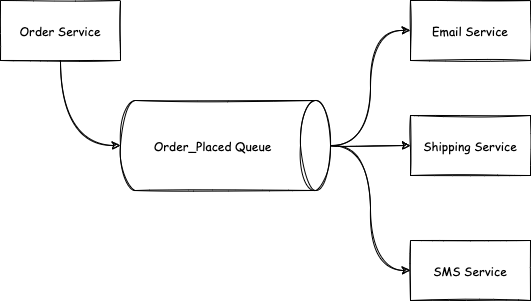
In Asynchronous messaging, a microservice sends a message to another microservice through a queuing system. a microservice publishes the message to a queue, the queuing system delivers the message to the recipient microservice ( consumer).
There are some advantages of asynchronous messaging over synchronous point-to-point communication.
- Recipient microservice (Consumer) need not be available all the time. if a consumer goes offline due to failure, messages are retained in the queue and once the consumer is online, pending messages are delivered and processed in an ordered fashion.
- Multiple consumers subscribe to a queue. Each consumer gets their copy.
- Multiple instances of a consumer could distribute the load.
Non-Blocking Processing
In synchronous processing, During I/O operation like an HTTP post request, Thread waits for I/O operation to get completed and resumes processing next instruction after I/O operation. These kinds of I/O operations are called blocking I/O.
In non-Blocking processing, Pool of Threads runs the application. During I/O operation Threads do not wait for I/O operation to get over but joins the Thread pool. When the I/O operation completes, a thread is popped from the Thread pool to process the next instruction. The popped Thread could be any other thread or the same Thread that initiated I/O.
Non-Blocking processing optimizes resource utilization as Thread does multiple operations rather than waiting for blocking I/O operation. Hence system I/O throughput increases, the system could serve more requests concurrently.
Deployment with Immutable Infrastructure
An immutable infrastructure is an approach where a newer version of application deployment replaces the previous version rather than updating it.
In immutable infrastructure, always new container or VM or hardware is provisioned for new version of application.
Rolling-Update and Recreate are popular strategies for deployments.
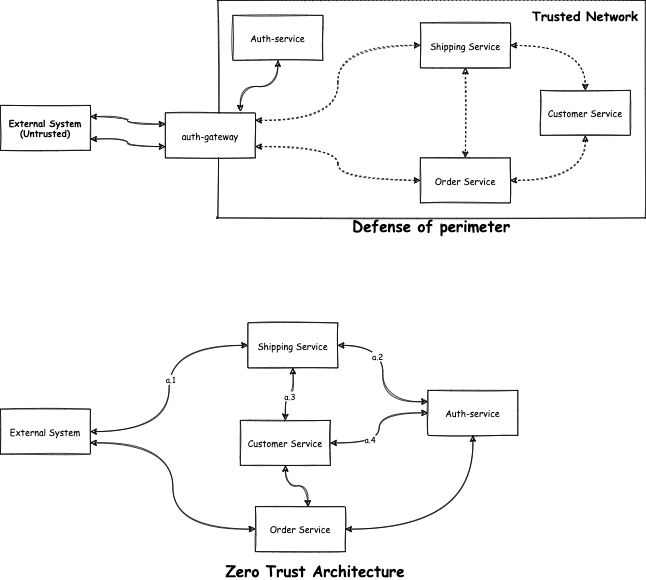
Zero trust architecture for security
Defense of perimeter is a popular concept where a network boundary is created around private systems. Auth Gateways act as a gatekeeper to provide access to private and internal systems. Internal private systems that communicate internally are not required to have access control. It has been observed that most of the security incidents reported were compromised via internal systems.
Zero Trust Architecture is a concept where a system must not trust another system or user based on internal or external to its perimeter. In simpler words, each system must authenticate and authorize every request irrespective of network or organization perimeter.
Distributed logging
Troubleshooting and debugging issues in the microservice architecture are difficult as requests and responses pass through multiple systems. A centralized and externalized logging system is used for all the logs. All microservice sends log messages with a Correlation ID to the logging system, where system logs are analyzed.
Designing system for failure recovery not to avoid failures
Design the system keeping in mind that failure will occur and the system must recover from it. For example, A microservice must restart itself in case of memory overflow.
MTBF and MTTR are popular parameters to measure the system reliability of repairable systems.
MTBF (mean-time-between-failures) is used to know the expected time between two failures for a repairable system.
MTTR (mean-time-to-recover) is used to predict the expected time to recover after failure.
Conclusion
Designing application for elastic load makes the system complex and increases development and maintenance costs. Not all applications require to handle the elastic load. Some applications are built for a smaller user group e.g. employee management system, where it is unlikely to have a high load, as the increase in employees will not happen overnight.
Usually, applications that are exposed to the public domain, require to handle such a huge load and unpredictable events.